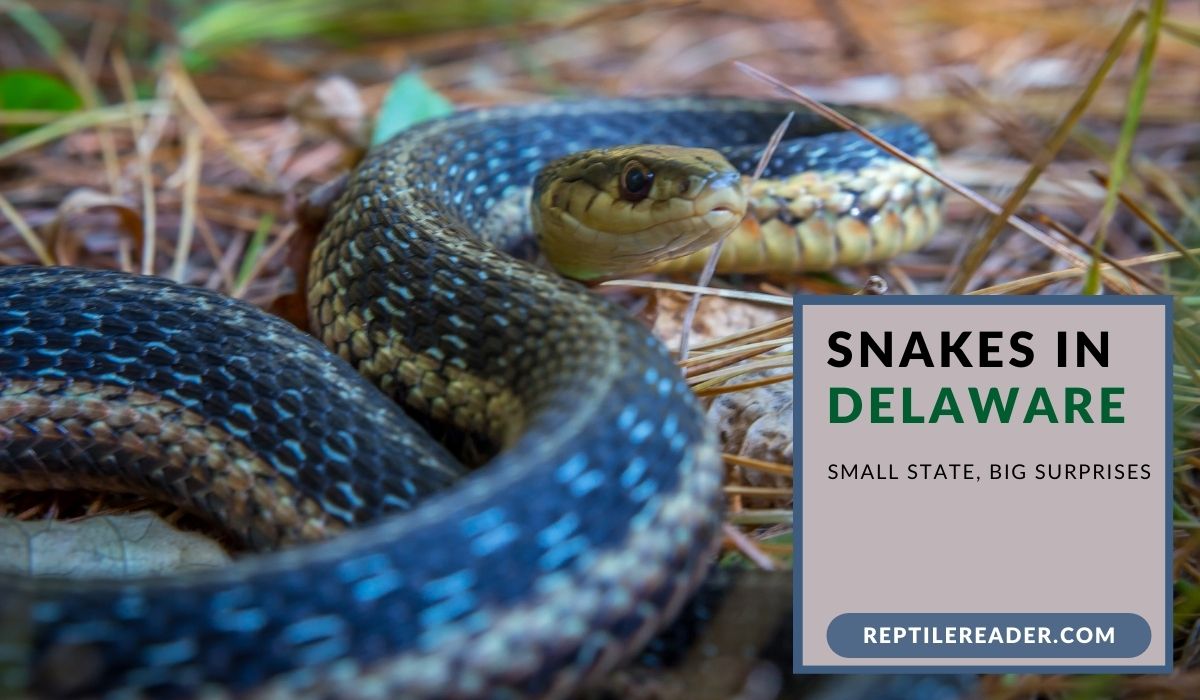
Snakes in Delaware: Small State, Big Surprises
Greetings, dear readers. In the small but intriguing state of Delaware, we find ourselves amidst a diverse array of 20 snake species, each with its own unique characteristics and habitats.
From the venomous copperhead to the elusive eastern hognose, these reptiles of Delaware reveal a captivating world that often goes unnoticed. Rest assured, the majority of these serpents are nonvenomous and would rather keep to themselves.
So, let us embark on a journey through the wilds of Delaware, as we uncover the intriguing lives and behaviors of these fascinating creatures that call this state their home.
| # | Name | Details | Image |
| 1 | Black Racer (Coluber constrictor constrictor) |
|  |
| 2 | Black Rat Snake (Pantherophis obsoletus) |
|  |
| 3 | Common Water Snake (Nerodia sipedon) |
|  |
| 4 | Copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) |
|  |
| 5 | Corn Snake (Pantherophis guttatus) |
|  |
| 6 | Eastern Garter Snake (Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis) |
|  |
| 7 | Eastern Milksnake (Lampropeltis triangulum) |
|  |
| 8 | Eastern Worm Snake (Carphophis amoenus amoenus) |
|  |
| 9 | Kingsnake (Lampropeltis getula) |
|  |
| 10 | Northern Brown Snake (Storeria dekayi) |
|  |
| 11 | Northern Ringneck Snake (Diadophis punctatus edwardsii) |
|  |
| 12 | Northern Water Snake (Nerodia sipedon) |
|  |
| 13 | Plain-bellied Watersnake (Nerodia erythrogaster) |
|  |
| 14 | Queen Snake (Regina septemvittata) |
|  |
| 15 | Red-Bellied Snake (Storeria occipitomaculata) |
|  |
| 16 | Ribbon Snake (Thamnophis sauritus) |
|  |
| 17 | Rough Green Snake (Opheodrys aestivus) |
|  |
| 18 | Scarlet Snake (Cemophora coccinea) |
|  |
| 19 | Smooth Earth Snake (Virginia valeriae) |
|  |
| 20 | Timber Rattlesnake (Crotalus horridus) |
|  |
20 Snakes You Can Find in Delaware
In the state of Delaware, a fascinating array of serpents can be found slithering through its diverse landscapes. From venomous to harmless, each species has its unique story to tell. Below, we’ll explore the wonders of these often misunderstood creatures of Delaware, from their natural habitats and behaviors to the challenges they face in our changing world.
1. Black Racer
- Scientific Name: Coluber constrictor constrictor
- Common Name: Black racer
- Size: Up to 6 feet (1.8 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas
- Color: Solid black with white chin
- Habitat: Various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 6 feet (1.8 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, lizards, frogs, and insects
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 12-30
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Black Racer (Coluber constrictor constrictor) is a non-venomous snake species of Delaware reaching up to 6 feet (1.8 meters) in length, featuring a solid black coloration and a striking white chin. It thrives in an array of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas. As a diurnal and swift-moving snake, it feeds on rodents, lizards, frogs, and insects. They reproduce by laying eggs in clutches of 12-30, and are currently designated as a species of least concern in terms of conservation status.
2. Black Rat Snake
- Scientific Name: Pantherophis obsoletus
- Common Name: Black rat snake
- Size: Up to 8 feet (2.4 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and urban areas
- Color: Black with faint dark blotches
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and urban areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 8 feet (2.4 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, birds, and eggs
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 5-30
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
Pantherophis obsoletus, commonly known as Black Rat Snake, can grow up to 8 feet (2.4 meters) long, with a black and dark-blotched coloring. These non-venomous reptiles inhabit forests, grasslands, and urban areas of Delaware, showcasing diurnal and semi-arboreal behavior. Their diet consists of rodents, birds, and eggs. Female Black Rat Snakes lay eggs in clutches of 5-30 during the reproduction season. Although not endangered, these snakes play an important role in controlling rodent populations.
3. Common Water Snake
- Scientific Name: Nerodia sipedon
- Common Name: Common water snake
- Size: Up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Aquatic habitats, including lakes, rivers, and ponds
- Color: Brown or gray with dark bands or blotches
- Habitat: Aquatic habitats, including lakes, rivers, and ponds
- Maximum Size: Up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters)
- Diet: Fish, frogs, and salamanders
- Reproduction: Give birth to live young in litters of 10-40
- Venom: Non-venomous, but can release a foul-smelling musk
- Conservation: Least concern
The Common Water Snake (Nerodia sipedon) is a non-venomous, nocturnal, semiaquatic reptile that can grow up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters) in size. Their brown or gray body has dark bands or blotches as markings. Commonly found in aquatic habitats like lakes, rivers, and ponds, this snake’s diet consists of fish, frogs, and salamanders. It reproduces by giving birth to live young in litters containing 10-40 offspring. Although non-venomous, it can release foul-smelling musk in defense. Its conservation status is of least concern.
4. Copperhead
- Scientific Name: Agkistrodon contortrix
- Common Name: Copperhead
- Size: Up to 3 feet (0.9 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, swamps, rocky terrain, and riverside habitats
- Color: Coppery-brown with reddish-brown or dark hourglass-shaped bands
- Habitat: Forests, swamps, rocky terrain, and riverside habitats
- Maximum Size: Up to 3 feet (0.9 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, birds, frogs, and insects
- Reproduction: Give live birth to 2-18 young in late summer or early fall
- Venom: Venomous, but relatively mild compared to other venomous snakes
- Conservation: Least concern
The Copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) is a venomous snake up to 3 feet (0.9 meters) long, known for its coppery-brown coloring with reddish-brown or dark hourglass-shaped bands. Inhabiting forests, swamps, rocky terrain, and riverside habitats, these solitary and primarily nocturnal creatures prey on rodents, birds, frogs, and insects. Copperheads give live birth to 2-18 young in late summer or early fall. Though venomous, their venom is relatively mild compared to other venomous snakes. Their conservation status is of least concern.
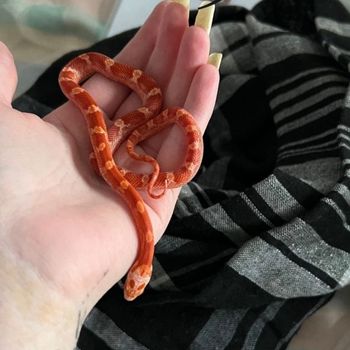
5. Corn Snake
- Scientific Name: Pantherophis guttatus
- Common Name: Corn snake
- Size: 24-72 inches (61-183 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Woodlands, grasslands, and abandoned buildings
- Color: Orange or brownish-yellow with red or brown blotches
- Habitat: Woodlands, grasslands, and abandoned buildings
- Maximum Size: 24-72 inches (61-183 cm)
- Diet: Rodents, birds, and eggs
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 10-30
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Corn Snake (Pantherophis guttatus) is a non-venomous North American species, ranging from 24-72 inches in length. Their striking coloration consists of an orange or brownish-yellow base with red or brown blotches. Inhabiting woodlands, grasslands, and abandoned buildings, these nocturnal and terrestrial creatures feed primarily on rodents, birds, and eggs. Corn Snakes reproduce by laying egg clutches of 10-30, and have a conservation status of Least Concern.
6. Eastern Garter Snake
- Scientific Name: Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis
- Common Name: Eastern garter snake
- Size: Up to 2-4.5 feet (0.6-1.4 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, grasslands, wetlands, and urban areas
- Color: Brown, green or gray with three yellow stripes
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, wetlands, and urban areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 2-4.5 feet (0.6-1.4 meters)
- Diet: Earthworms, amphibians, fish, and small mammals
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 10-40
- Venom: Mildly venomous but harmless to humans
- Conservation: Least concern
The Eastern Garter Snake (Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis) is a commonly found snake species that can grow up to 2-4.5 feet (0.6-1.4 meters) in length. It displays a brown, green, or gray coloration adorned with three yellow stripes. Inhabitants of forests, grasslands, wetlands and urban areas, these diurnal and terrestrial reptiles primarily feed on earthworms, amphibians, fish, and small mammals. Eastern Garter Snakes reproduce by laying 10-40 eggs per clutch, and although they are mildly venomous, their venom poses little risk to humans. They are currently classified under the least concern category in conservation status.
7. Eastern Milksnake
- Scientific Name: Lampropeltis triangulum
- Common Name: Eastern milksnake
- Size: Up to 3.9 feet (1.2 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, grasslands, farmlands, and rocky areas
- Color: Reddish-brown with y-shaped black-edged white bands
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, farmlands, and rocky areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 3.9 feet (1.2 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, small birds, and reptiles
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 3-20
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Eastern Milksnake (Lampropeltis triangulum) is a non-venomous snake that grows up to 3.9 feet (1.2 meters) in length. It features a reddish-brown color adorned with Y-shaped black-edged white bands. Commonly found in forests, grasslands, farmlands, and rocky areas of Delaware, this nocturnal and terrestrial snake primarily consumes rodents, small birds, and reptiles. Eastern Milksnakes reproduce by laying egg clutches of 3-20. Currently, their conservation status is listed as least concern.
8. Eastern Worm Snake
- Scientific Name: Carphophis amoenus amoenus
- Common Name: Eastern worm snake
- Size: Up to 11-14 inches (28-35.5 centimeters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and grasslands with moist soil
- Color: Pink-brown to gray-brown with a pinkish-yellow belly
- Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and grasslands with moist soil
- Maximum Size: Up to 11-14 inches (28-35.5 centimeters)
- Diet: Earthworms and other soft-bodied invertebrates
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 2-8
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Eastern Worm Snake (Carphophis amoenus amoenus) is a small, non-venomous species, reaching lengths of 11-14 inches (28-35.5 centimeters). It possesses a pink-brown to gray-brown coloration with a distinctive pinkish-yellow belly. This elusive, nocturnal burrower inhabits forests, woodlands, and grasslands with moist soil. Its diet primarily consists of earthworms and other soft-bodied invertebrates. The Eastern Worm Snake lays egg clutches of 2-8 eggs, and its conservation status is currently listed as “Least Concern.”
9. Kingsnake
- Scientific Name: Lampropeltis getula
- Common Name: Kingsnake
- Size: Up to 8 feet (2.4 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts
- Color: Black or dark brown with white or yellow bands
- Habitat: Various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts
- Maximum Size: Up to 8 feet (2.4 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, birds, lizards, and other snakes
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 3-24
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Kingsnake (Lampropeltis getula) is a strikingly banded reptile found in various habitats, such as forests, grasslands, and deserts. Measuring up to 8 feet (2.4 meters) in length, they feature black or dark brown scales contrasted by white or yellow bands. As nocturnal, terrestrial creatures, Kingsnakes are also adept climbers. Their diet consists of rodents, birds, lizards, and other snakes. Though non-venomous, their reproduction entails laying 3-24 eggs per clutch. Their conservation status is currently least concern.
10. Northern Brown Snake
- Scientific Name: Storeria dekayi
- Common Name: Northern brown snake
- Size: Up to 20 inches (51 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Various habitats, including wetlands, forests, and suburban areas
- Color: Brown or grayish-brown with a lighter stripe down the back
- Habitat: Various habitats, including wetlands, forests, and suburban areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 20 inches (51 cm)
- Diet: Earthworms, snails, and soft-bodied insects
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in small clutches of 3-30
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Northern Brown Snake (Storeria dekayi) is a non-venomous reptile growing up to 20 inches (51 cm) in length, with a brown or grayish-brown coloration and a lighter stripe down its back. It can be found inhabiting wetlands, forests, and suburban areas across various regions. With primarily diurnal behavior, this snake hides during the day, foraging at night for earthworms, snails, and soft-bodied insects. Mating results in small clutches of 3-30 eggs. Its conservation status is currently listed as least concern.
11. Northern Ringneck Snake
- Scientific Name: Diadophis punctatus edwardsii
- Common Name: Northern ringneck snake
- Size: 12-15 inches, rarely up to 24 inches
- Natural Habitat: Woodlands, rock outcrops, and grasslands
- Color: Gray or black with a distinctive yellow or orange ring around the neck
- Habitat: Woodlands, rock outcrops, and grasslands
- Maximum Size: 12-15 inches, rarely up to 24 inches
- Diet: Small invertebrates, slugs, earthworms, and small amphibians
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 3-10
- Venom: Mildly venomous, but harmless to humans
- Conservation: Least concern
The Northern Ringneck Snake (Diadophis punctatus edwardsii) is a small, mildly venomous snake native to North America, measuring 12-15 inches in length, rarely reaching up to 24 inches. Its body color varies from gray to black and features a distinctive yellow or orange ring around its neck. The species inhabits woodlands, rock outcrops, and grasslands, exhibiting nocturnal, secretive, and terrestrial behavior. Its diet consists of small invertebrates, slugs, earthworms, and small amphibians. These snakes reproduce by laying egg clutches of 3-10 and pose no threat to humans. Their conservation status is listed as least concern.
12. Northern Water Snake
- Scientific Name: Nerodia sipedon
- Common Name: Northern water snake
- Size: Up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Aquatic habitats, such as rivers, lakes, ponds, and marshes
- Color: Brown or gray with dark bands or blotches
- Habitat: Aquatic habitats, such as rivers, lakes, ponds, and marshes
- Maximum Size: Up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters)
- Diet: Fish, amphibians, and invertebrates
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 10-30
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Northern Water Snake (Nerodia sipedon) is a non-venomous reptile that can grow up to 4.5 feet (1.4 meters) in length. It is characterized by its brown or gray color with dark bands or blotches. This nocturnal and semi-aquatic species can be found in a variety of aquatic habitats, including rivers, lakes, ponds, and marshes. Its diet consists of fish, amphibians, and invertebrates. Northern Water Snakes reproduce by laying eggs in clutches of 10-30, and currently have a conservation status of least concern.
13. Plain-bellied Watersnake
- Scientific Name: Nerodia erythrogaster
- Common Name: Plain-bellied watersnake
- Size: 24-40 inches (61-102 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands
- Color: Olive, brown, or gray with a yellow, orange, or red unmarked belly
- Habitat: Rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands
- Maximum Size: 24-40 inches (61-102 cm)
- Diet: Fish, frogs, and other amphibians
- Reproduction: Live-bearing; 5-29 offspring per litter
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Plain-bellied Watersnake (Nerodia erythrogaster) is a semi-aquatic, non-venomous snake measuring 24-40 inches (61-102 cm) in length. It features an olive, brown, or gray coloration with a distinct yellow, orange, or red unmarked belly. As adept swimmers, they inhabit rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands, with diurnal behavior. Their diet primarily consists of fish, frogs, and other amphibians. These snakes are live-bearing, producing 5-29 offspring per litter. Currently, their conservation status is of least concern.
14. Queen Snake
- Scientific Name: Regina septemvittata
- Common Name: Queen snake
- Size: Up to 3 feet (0.9 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Streams, creeks, and other aquatic environments
- Color: Olive, brown or gray with three stripes and cream or yellowish belly
- Habitat: Streams, creeks, and other aquatic environments
- Maximum Size: Up to 3 feet (0.9 meters)
- Diet: Crayfish and other small aquatic invertebrates
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 4-14
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Queen Snake (Regina septemvittata) is a non-venomous reptile growing up to 3 feet (0.9 meters) in length. Often sporting olive, brown, or gray coloration, this snake displays three distinctive stripes and a yellowish belly. It thrives in aquatic habitats such as streams and creeks, and is highly active during the day. Queen Snakes primarily feed on crayfish and other small aquatic invertebrates. They lay eggs in clutches of 4-14, and currently face no significant conservation threats.
15. Red-Bellied Snake
- Scientific Name: Storeria occipitomaculata
- Common Name: Red-bellied snake
- Size: 8-16 inches (20-41 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and wetlands
- Color: Gray or brown with a red or orange belly
- Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and wetlands
- Maximum Size: 8-16 inches (20-41 cm)
- Diet: Slugs, snails, and earthworms
- Reproduction: Live-bearing; 4-21 offspring per litter
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Red-Bellied Snake (Storeria occipitomaculata) is a small, non-venomous snake measuring 8-16 inches (20-41 cm) in length. They are gray or brown with a distinctive red or orange belly. Mostly found in forests, woodlands, and wetlands of Delaware, these nocturnal and secretive creatures primarily feed on slugs, snails, and earthworms. As live-bearing reptiles, they produce 4-21 offspring in each litter. With a conservation status of “Least Concern,” this terrestrial snake presents no significant threat to humans.
16. Ribbon Snake
- Scientific Name: Thamnophis sauritus
- Common Name: Eastern ribbon snake
- Size: 18-36 inches (45-91 centimeters)
- Natural Habitat: Wetland habitats such as marshes, swamps, and streams
- Color: Black or dark brown with thin, yellow or white stripes
- Habitat: Wetland habitats such as marshes, swamps, and streams
- Maximum Size: 18-36 inches (45-91 centimeters)
- Diet: Amphibians, small fish, and invertebrates
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 3-26
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Eastern Ribbon Snake (Thamnophis sauritus) is a non-venomous species of slender, fast-moving reptile measuring 18-36 inches (45-91 centimeters) in length. Its coloration includes black or dark brown tones with thin, yellow or white stripes. This snake thrives in wetland habitats such as marshes, swamps, and streams. Active during the day, it is a strong swimmer that feeds primarily on amphibians, small fish, and invertebrates. Reproducing through egg-laying, it is currently classified as a species of least concern conservation-wise.
17. Rough Green Snake
- Scientific Name: Opheodrys aestivus
- Common Name: Rough green snake
- Size: 22-32 inches (56-81 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and areas near water sources
- Color: Bright green with a lighter belly
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and areas near water sources
- Maximum Size: 22-32 inches (56-81 cm)
- Diet: Insects and spiders
- Reproduction: Lay eggs in clutches of 3-12
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Rough Green Snake (Opheodrys aestivus) is a vibrant, non-venomous reptile that measures between 22-32 inches (56-81 cm) in length. Its dazzling bright green coloration is accentuated by a lighter belly, making it well-camouflaged in its preferred habitats of forests, grasslands, and areas near water sources. Known for their diurnal, arboreal behavior, these skillful climbers of Delaware primarily consume insects and spiders. Rough Green Snakes reproduce by laying clutches of 3-12 eggs, and their conservation status is currently classified as least concern.
18. Scarlet Snake
- Scientific Name: Cemophora coccinea
- Common Name: Scarlet snake
- Size: Up to 20-30 inches (50-76 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and suburban areas
- Color: Red or orangish with black bands and a white or yellowish underbelly
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, and suburban areas
- Maximum Size: Up to 20-30 inches (50-76 cm)
- Diet: Reptile eggs, small rodents, and lizards
- Reproduction: Lays eggs in clutches of 3-8
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Scarlet Snake (Cemophora coccinea) is a non-venomous, nocturnal reptile found in forests, grasslands, and suburban areas. Measuring up to 20-30 inches (50-76 cm) in length, it features striking red or orangish scales with black bands and a white or yellowish underbelly. This burrowing snake has a diet consisting of reptile eggs, small rodents, and lizards. Females lay eggs in clutches of 3-8. With a conservation status of least concern, the Scarlet Snake continues to thrive in its habitats.
19. Smooth Earth Snake
- Scientific Name: Virginia valeriae
- Common Name: Smooth earth snake
- Size: 7-10 inches (18-25 cm)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and grasslands
- Color: Brown or gray with a lighter belly
- Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and grasslands
- Maximum Size: 7-10 inches (18-25 cm)
- Diet: Earthworms, slugs, and insects
- Reproduction: Live-bearing; 3-10 offspring per litter
- Venom: Non-venomous
- Conservation: Least concern
The Smooth Earth Snake (Virginia valeriae) is a small, non-venomous reptile measuring 7-10 inches (18-25 cm) in length. It has a brown or gray coloration, with a lighter belly, and inhabits forests, woodlands, and grasslands. This secretive, nocturnal snake is known for burrow-dwelling and primarily feasts on earthworms, slugs, and insects. The species is live-bearing, producing 3-10 offspring per litter. With a conservation status of “Least Concern,” the Smooth Earth Snake population remains relatively stable.
20. Timber Rattlesnake
- Scientific Name: Crotalus horridus
- Common Name: Timber rattlesnake
- Size: Up to 6 feet (1.8 meters)
- Natural Habitat: Forests, mixed woodlands, and rocky hillsides
- Color: Yellow, brown, gray, or black with dark bands
- Habitat: Forests, mixed woodlands, and rocky hillsides
- Maximum Size: Up to 6 feet (1.8 meters)
- Diet: Rodents, birds, and small mammals
- Reproduction: Viviparous, giving birth to 4-14 live young
- Venom: Hemotoxic venom
- Conservation: Least concern
The Timber Rattlesnake, scientifically known as Crotalus horridus, is a solitary, ambush predator that can grow up to 6 feet (1.8 meters) in length. It comes in various colors, including yellow, brown, gray, or black with dark bands, and inhabits forests, mixed woodlands, and rocky hillsides. Its diet consists of rodents, birds, and small mammals. Unlike most snakes, the Timber Rattlesnake is viviparous, giving birth to 4-14 live young. It possesses hemotoxic venom, and its conservation status is currently listed as least concern.
Nearby States:
Final Words
All the 20 snakes have truly opened our eyes to the fascinating world of snakes found in Delaware. Who knew there were so many different types of these slithering reptiles, each with their own unique characteristics and habitats?
Not only did we get a chance to learn about some of the more common and well-known species, but we also delved into the lesser-known and often misunderstood ones.
So, the next time you’re out and about in Delaware, keep an eye out for these incredible creatures, and let’s continue to appreciate and protect the diverse wildlife that makes our world so interesting!
Are the Snakes Found in New Hampshire Also Present in Delaware?
Both New Hampshire and Delaware are home to a variety of snake species, but there are regional differences in their environments. Some species of snakes in nh, such as the Timber Rattlesnake, are not found in Delaware, while common species like the garter snake can inhabit both areas.
Are Snakes from Delaware Legal to Keep as Pets and Where Can I Get Them?
In Delaware, it is legal to keep non-venomous snakes as pets, but certain species may require a permit. The cost of petco snakes in Delaware varies depending on the breed and size. Reputable breeders and exotic pet stores are good places to find snakes as pets.